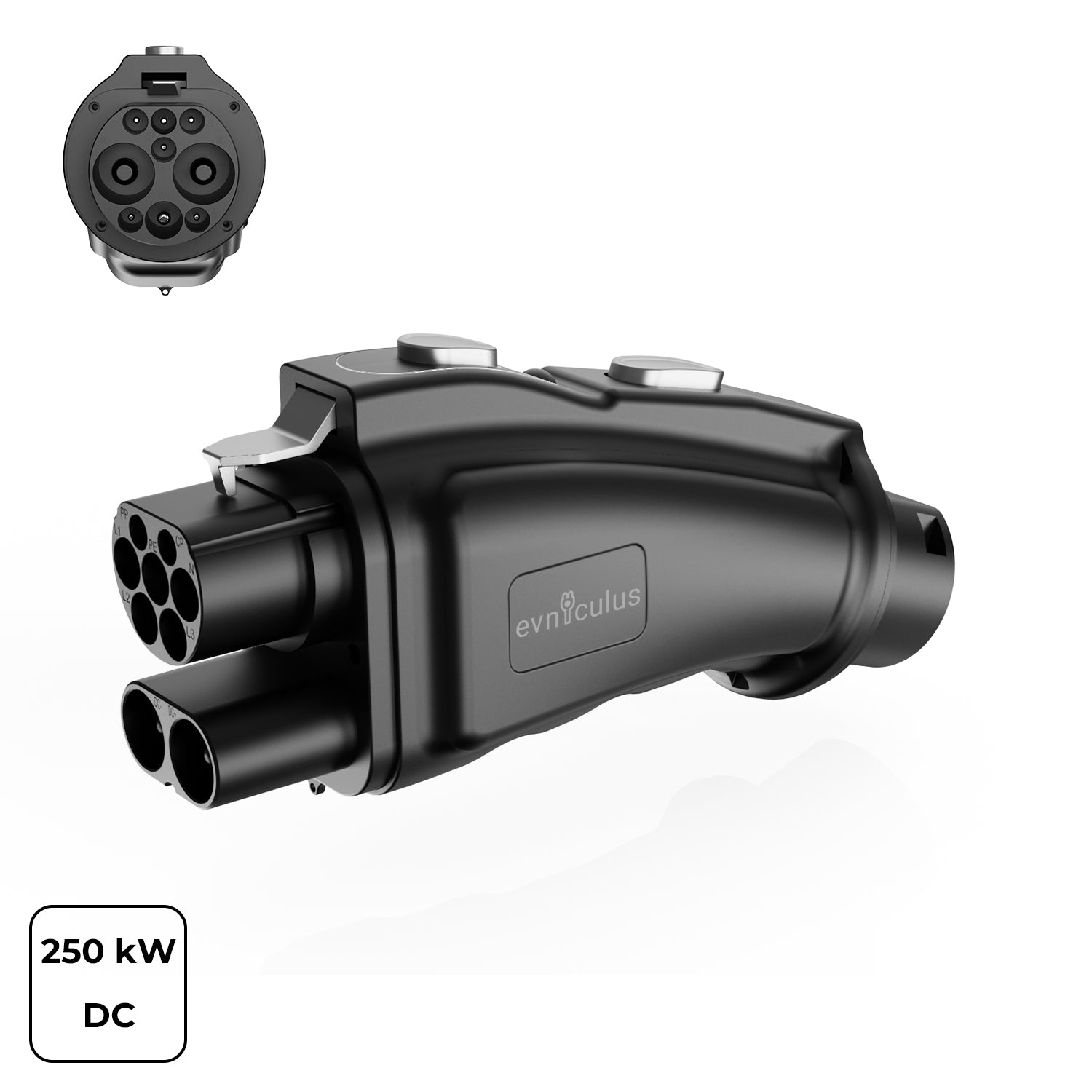
Understanding Different EV Charging Plug Standards
Confused by all the different EV charging plug standards and which one will actually fit into your electric vehicle? Almost too many options exist: CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla plugs. The world of EV charging can be very confusing for many.
But don't worry; this article makes things a bit easier. We will break down the different charging standards, explain the differences between AC and DC charging, and take you through the options for both types of plugs.
By the end, you'll know what your EV needs to charge it and make choices that best fit for your lifestyle.
So, let's get started.
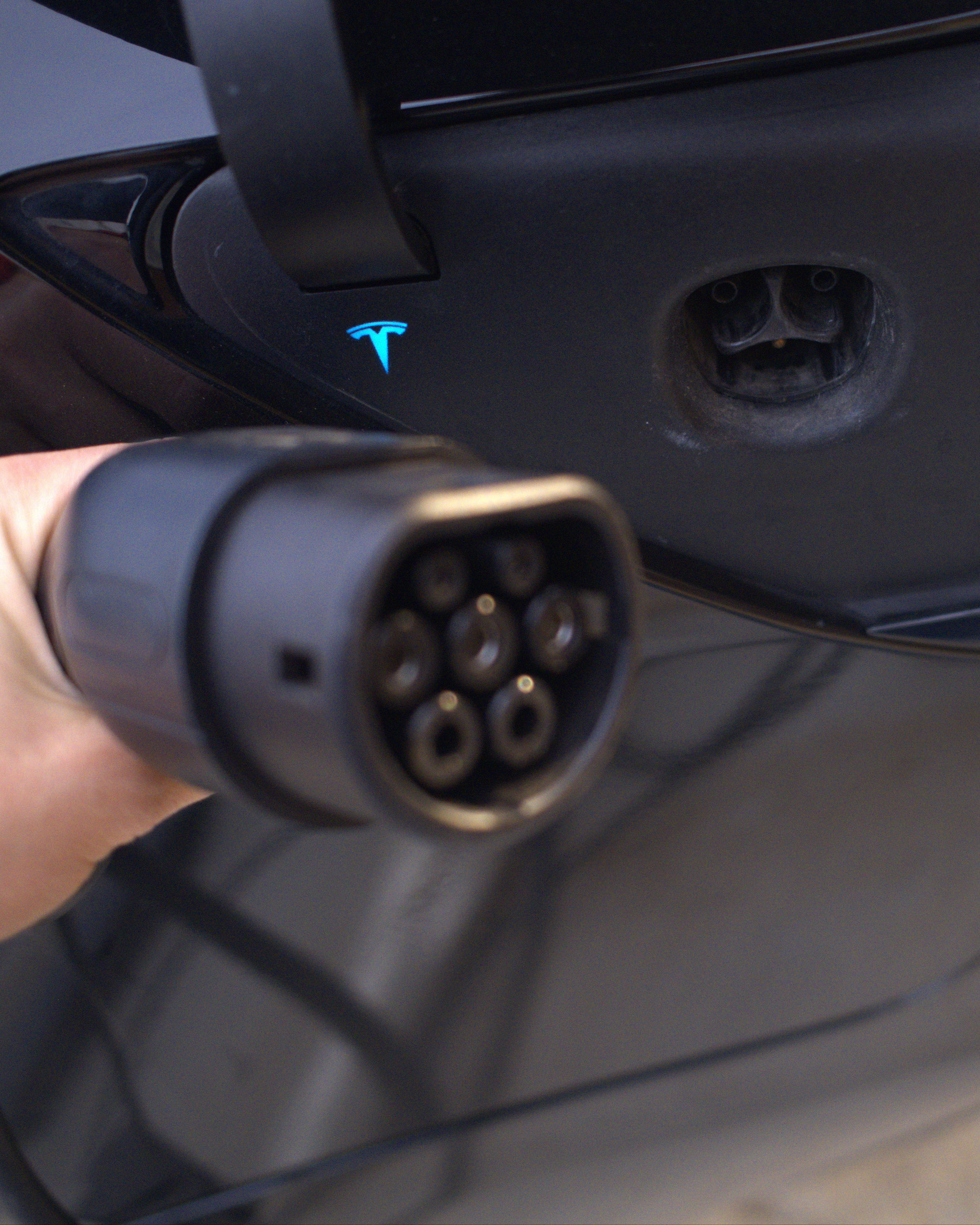

What are EV charging standards?
EV charging standards refer to the specific types of plugs and connectors used to charge electric vehicles. These work to ensure compatibility between the charging station and the EV, hence providing a reliable and safe charging experience. As electric vehicles gain popularity around the world, different regions and manufacturers are implementing various standards that suit their markets and technologies well.
Simplified, the EV charging standards define how energy flows from the charging station into your car. They involve everything from physical plug designs to communication protocols involved in allowing your EV and charger to "talk" to each other. These standards are relevant as one selects the appropriate charger, mainly if you travel across regions or own a vehicle with features from a specific manufacturer.
Direct current vs alternating current charging
There are the two types of electricity you will come across in charging your electric vehicle: direct current and alternating current. Both will be important to understand for the simple reason that it shows how fast your EV charges.
- AC: This is the type of power that comes off the grid, such as what you use in your home. The reason AC chargers are slower is because it has to be converted inside your car to DC to charge the battery. AC charging works well for everyday applications, like charging over night at home or at work.
- DC: These are also known as fast chargers; the power directly goes to the car's battery without the need to convert. That is why, in most cases, charging takes less than 20 minutes to get up to 80%. You'll usually find DC chargers at public stations, especially on highways.
AC works best for steady, slow charging, whereas DC is ideal for fast charging when you are on the move.
AC charging standards
AC charging standards greatly vary depending on a region and the type of electric vehicle. The standards are responsible for designing the plug and showing how electricity reaches your car. Here are the most common AC charging plug types:
Type 1 Charging
Type 1 plugs, also known as J1772 or SAE J1772, this is a common type in North America and Japan. All these are single-phase, meaning only slower speeds can be accommodated. These normally are found in residential charging installations or lower-power public charge points.
- Charging Speed: Up to 7.4 kW.
- Best For: Home charging and short daily commutes.
- Connector: A compact five-pin design.
Type 1 plugs are easy and available to use for most of the early-generation EVs.
Type 2 Charging
Type 2 plugs are standard in Europe and large parts of the world. They support single-phase and three-phase charging, enabling higher speeds. The majority of modern EVs in Europe use Type 2 for AC charging.
- Charging Speed: Up to 22 kW for residential setups and up to 43 kW at public stations.
- Best For: Home and public charging with faster speeds.
- Connector: A seven-pin design for better compatibility and performance.
Type 2 plugs are versatile and widely supported, making them a popular choice for many EV owners.
GB/T Charging
Today, GB/T AC is a standard used in China for the electric vehicle. It was actually designed for the Chinese market and is hardly used outside that country. The GB/T does support single-phase and three-phase AC charging, so it's flexible, just like Type 2.
- Charging Speed: Up to 22 kW.
- Best For: EV owners in China.
- Connector: A unique design specific to the region.
Each of these standards for AC charging has its moments in the sun, depending on where you live and what kind of EV you drive. The correct plug makes charging efficient and without any flare-ups.
DC charging standards
The DC charging standards represent fast charging, in which high-power electricity is directly delivered to your EV's battery. There are several types of DC plugs in the different regions and by manufacturers, each with its own level of compatibility and charging speed. Let's dwell on some of the most prevalent DC charging standards:
CCS1 Charging
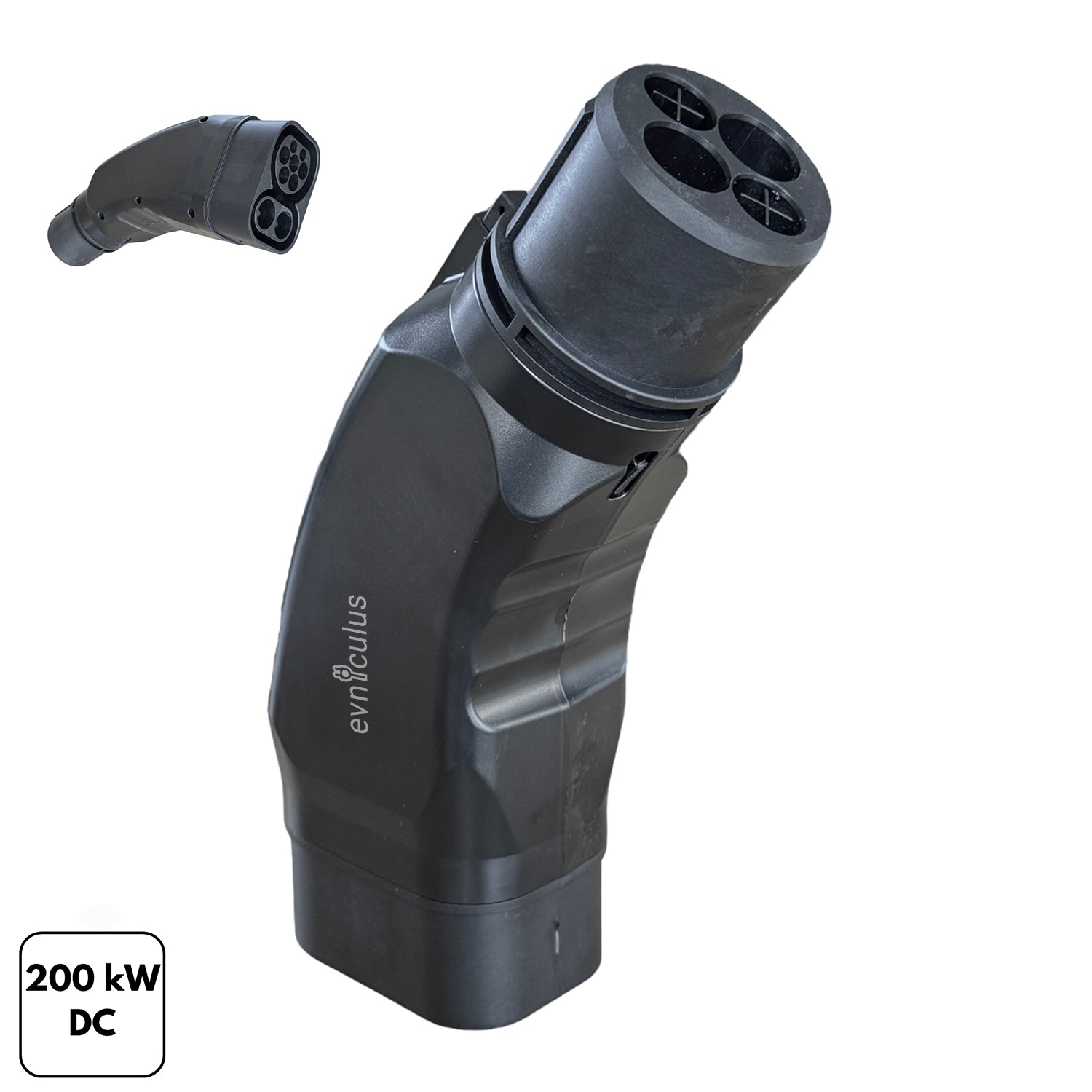
CCS1 refers to Combined Charging System 1 used in North America, adding two DC pins to the Type 1 AC connector; hence, it's able to charge both slowly and fast.
- Charging Speed: Up to 350 kW at compatible stations.
- Best For: EVs in North America requiring fast charging.
- Connector: Compact design with dual-purpose functionality.
CCS1 is ideal for EVs that need flexibility between AC and DC charging.
CCS2 Charging
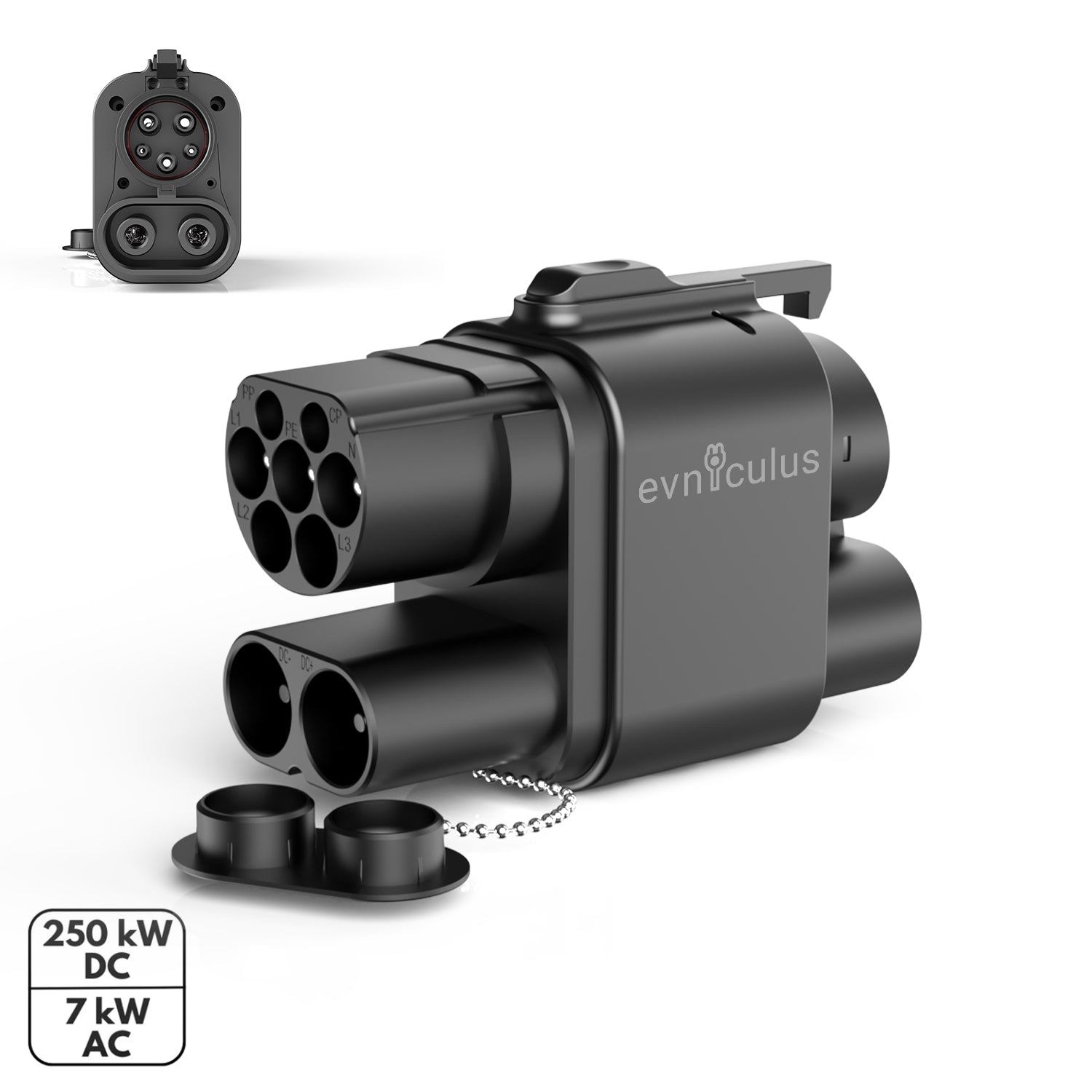
CCS2 is the standard for fast charging: the European counterpart to CCS1. This is a common type of connector in Europe and elsewhere, with a Type 2 AC plug combining with two DC pins that support everything from relatively slow to very fast rates.
- Charging Speed: Up to 350 kW, depending on the station.
- Best For: EVs in Europe and regions adopting Type 2 AC charging.
- Connector: Seven-pin design with additional DC pins.
CCS2 thus gets to offer smooth compatibility with both AC and DC charging networks and can be said to have gained more favor as a global standard.
CHAdeMO Charging
CHAdeMO is a popular DC charging standard from Japan, highly reputed for its reliability and bidirectional charging functionalities that allow vehicles not only to charge but also to supply power back to the grid.
- Charging Speed: Up to 400 kW for newer versions (up to 120 kW for older stations).
- Best For: Japanese EVs and vehicles supporting bidirectional charging.
- Connector: A large, round design with separate DC pins.
CHAdeMO isn't as common on new EVs these days, but it remains a tried-and-true backup for some brands like Nissan and Mitsubishi.
GB/T Fast Charging
GB/T DC Plug can be interpreted as a fast-charging standard in China. Unlike the GB/T AC plug, this one has been developed purely for high-speed DC charging.
- Charging Speed: Up to 250 kW or more at compatible stations.
- Best For: EVs in China requiring fast charging.
- Connector: Unique design tailored for the Chinese market.
Each of the DC charging standards has its application with respect to the model of the EV and the region. Knowing which plug your car supports will ensure a smooth and efficient charging experience.
Direct current vs alternating current charging
There are the two types of electricity you will come across in charging your electric vehicle: direct current and alternating current. Both will be important to understand for the simple reason that it shows how fast your EV charges.
- AC: This is the type of power that comes off the grid, such as what you use in your home. The reason AC chargers are slower is because it has to be converted inside your car to DC to charge the battery. AC charging works well for everyday applications, like charging over night at home or at work.
- DC: These are also known as fast chargers; the power directly goes to the car's battery without the need to convert. That is why, in most cases, charging takes less than 20 minutes to get up to 80%. You'll usually find DC chargers at public stations, especially on highways.
AC works best for steady, slow charging, whereas DC is ideal for fast charging when you are on the move.
AC charging standards
AC charging standards greatly vary depending on a region and the type of electric vehicle. The standards are responsible for designing the plug and showing how electricity reaches your car. Here are the most common AC charging plug types:
Type 1 Charging
Type 1 plugs, also known as J1772 or SAE J1772, this is a common type in North America and Japan. All these are single-phase, meaning only slower speeds can be accommodated. These normally are found in residential charging installations or lower-power public charge points.
- Charging Speed: Up to 7.4 kW.
- Best For: Home charging and short daily commutes.
- Connector: A compact five-pin design.
Type 1 plugs are easy and available to use for most of the early-generation EVs.
Type 2 Charging
Type 2 plugs are standard in Europe and large parts of the world. They support single-phase and three-phase charging, enabling higher speeds. The majority of modern EVs in Europe use Type 2 for AC charging.
- Charging Speed: Up to 22 kW for residential setups and up to 43 kW at public stations.
- Best For: Home and public charging with faster speeds.
- Connector: A seven-pin design for better compatibility and performance.
Type 2 plugs are versatile and widely supported, making them a popular choice for many EV owners.
GB/T Charging
Today, GB/T AC is a standard used in China for the electric vehicle. It was actually designed for the Chinese market and is hardly used outside that country. The GB/T does support single-phase and three-phase AC charging, so it's flexible, just like Type 2.
- Charging Speed: Up to 22 kW.
- Best For: EV owners in China.
- Connector: A unique design specific to the region.
Each of these standards for AC charging has its moments in the sun, depending on where you live and what kind of EV you drive. The correct plug makes charging efficient and without any flare-ups.
DC charging standards
The DC charging standards represent fast charging, in which high-power electricity is directly delivered to your EV's battery. There are several types of DC plugs in the different regions and by manufacturers, each with its own level of compatibility and charging speed. Let's dwell on some of the most prevalent DC charging standards:
CCS1 Charging
CCS1 refers to Combined Charging System 1 used in North America, adding two DC pins to the Type 1 AC connector; hence, it's able to charge both slowly and fast.
- Charging Speed: Up to 350 kW at compatible stations.
- Best For: EVs in North America requiring fast charging.
- Connector: Compact design with dual-purpose functionality.
CCS1 is ideal for EVs that need flexibility between AC and DC charging.
CCS2 Charging
CCS2 is the standard for fast charging: the European counterpart to CCS1. This is a common type of connector in Europe and elsewhere, with a Type 2 AC plug combining with two DC pins that support everything from relatively slow to very fast rates.
- Charging Speed: Up to 350 kW, depending on the station.
- Best For: EVs in Europe and regions adopting Type 2 AC charging.
- Connector: Seven-pin design with additional DC pins.
CCS2 thus gets to offer smooth compatibility with both AC and DC charging networks and can be said to have gained more favor as a global standard.
CHAdeMO Charging
CHAdeMO is a popular DC charging standard from Japan, highly reputed for its reliability and bidirectional charging functionalities that allow vehicles not only to charge but also to supply power back to the grid.
- Charging Speed: Up to 400 kW for newer versions (up to 120 kW for older stations).
- Best For: Japanese EVs and vehicles supporting bidirectional charging.
- Connector: A large, round design with separate DC pins.
CHAdeMO isn't as common on new EVs these days, but it remains a tried-and-true backup for some brands like Nissan and Mitsubishi.
GB/T Fast Charging
GB/T DC Plug can be interpreted as a fast-charging standard in China. Unlike the GB/T AC plug, this one has been developed purely for high-speed DC charging.
- Charging Speed: Up to 250 kW or more at compatible stations.
- Best For: EVs in China requiring fast charging.
- Connector: Unique design tailored for the Chinese market.
Each of the DC charging standards has its application with respect to the model of the EV and the region. Knowing which plug your car supports will ensure a smooth and efficient charging experience.
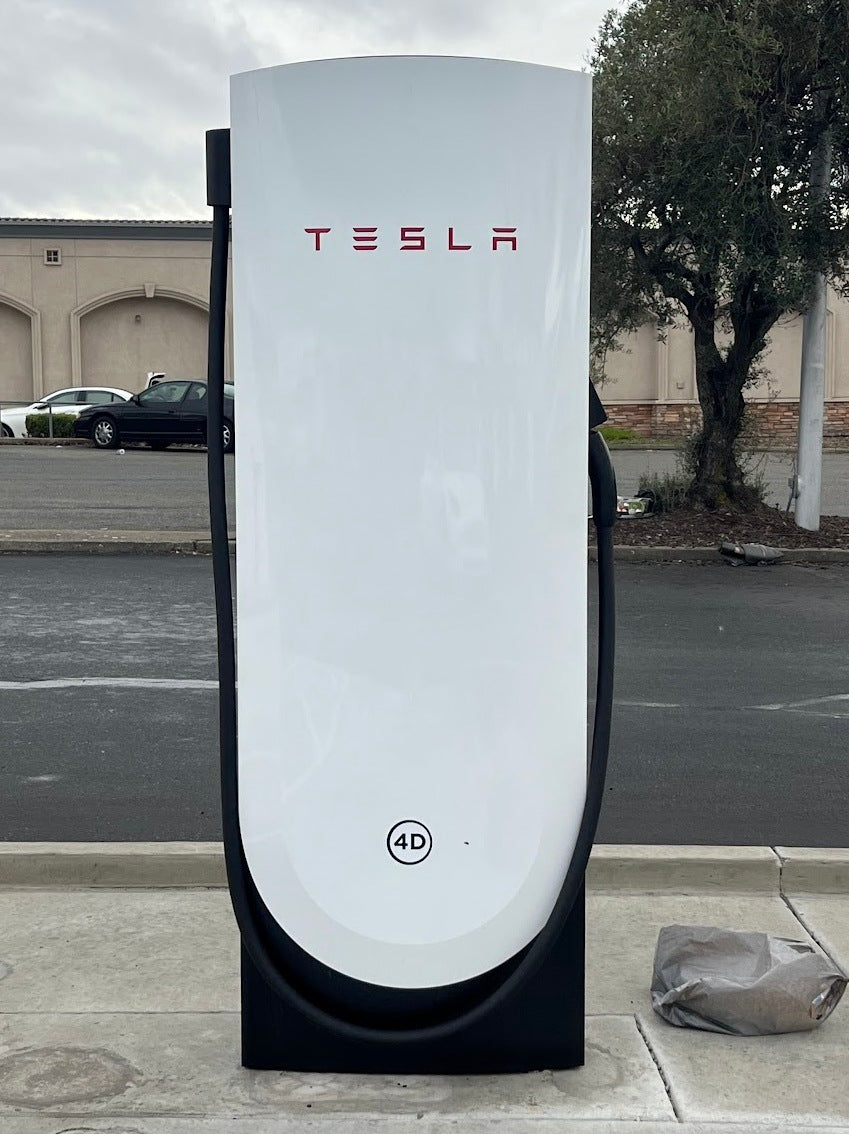

Tesla Supercharger
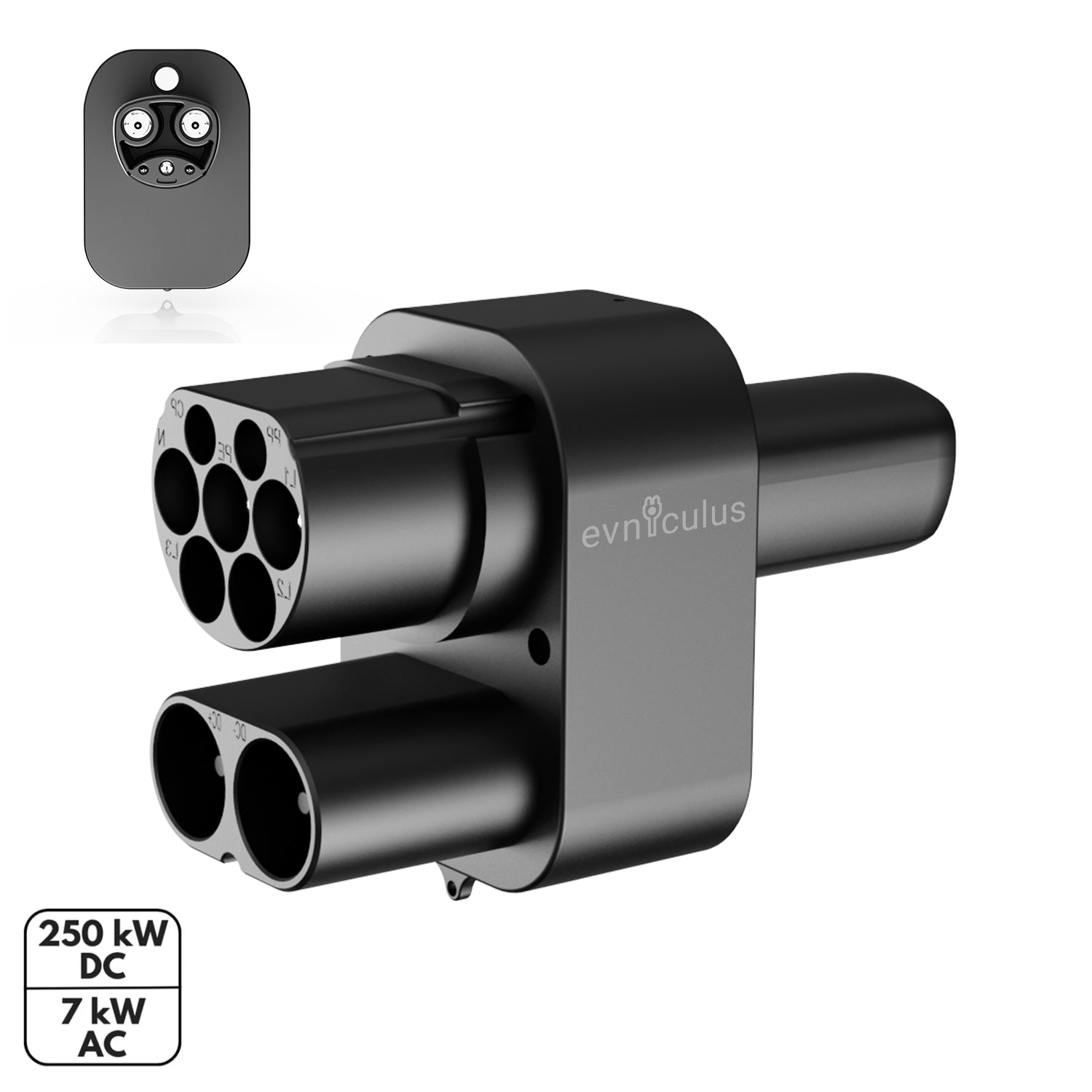
Tesla Superchargers create some of the most modern but highly recognizable fast-charging networks at the global level. Built specifically for Tesla vehicle models, these charging units are bound to provide high-speed DC recharging, an important ability that enables Tesla owners to refuel and get back on the road as soon as possible with a minimum loss of time.
- Charging Speed: Up to 500kW (with the 2025 V4 Superchargers. Only 800V vehicles such as the Cybertruck will be able to receive that much power).
- Best For: Tesla owners who need fast charging on long trips or during busy schedules.
- Connector: Tesla-specific plug in North America, called NACS, and CCS2 in Europe.
Tesla Superchargers are strategically located along highways, in urban centers, and near popular destinations for easy access by drivers. Besides the speed, ease brought by Tesla's network is also attributed to user-friendliness created by the use of the network. Tesla also has features such as integration into navigation to direct drivers where there is a Supercharger nearby while showing its availability in real-time.
This charging solution is called a vital part of the EV ecosystem as Tesla is gradually opening up its Supercharger network for other EV brands in selected regions.